SECTION 5: SUBSTANCE USE
Substance use was assessed based upon items in the Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance (YRBS).10 Youth were asked about their past-year experience with alcohol, marijuana, inhalants, and other drugs. The 4 items were inter-related (Wave 1 Cronbach’s alpha = 0.66). In Wave 2, an additional question about cigarette smoking was included (Wave 2 Cronbach’s alpha = 0.73; Wave 3 Cronbach’s alpha = 0.71).
Alcohol:
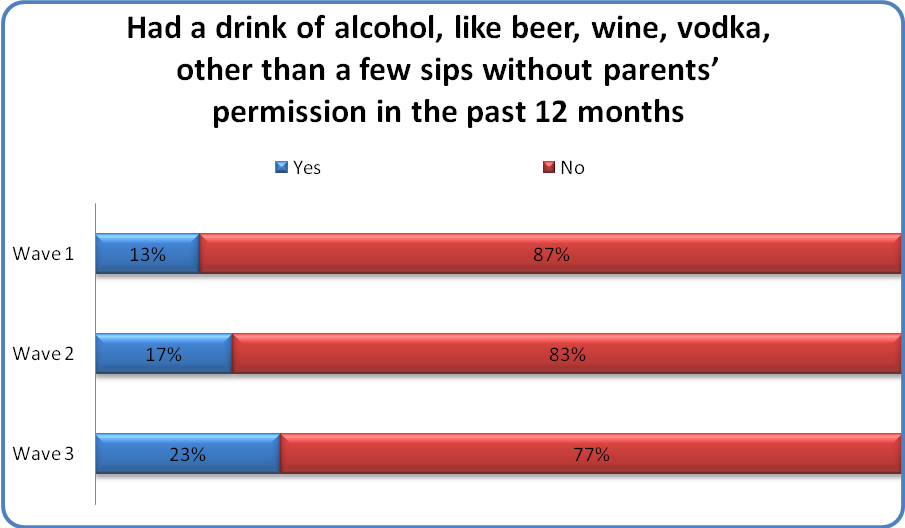
Among the substances queried, youth were most likely to say they had had a drink of alcohol without their parents’ permission in the past 12 months.
About 1 of every 10 youth reported consuming alcohol without their parent’s permission in the past 12 months. This increased to nearly 1 of every 4 youth in Wave 3 when the cohort was older. This is the most notable increase in substance use over time compared to other substances youth were asked about, suggesting that experimentation with alcohol may be the most normative among all of the substances.
Youth who had consumed alcohol in the past year (NWave1 = 182; NWave2 = 188; NWave3 = 264) were asked how old they were when they had their first drink of alcohol, other than a few sips, without their parents’ permission. Youth-reported age of first sip of alcohol increased by approximately one year with each Wave of the study, which is consistent with what one would expect given the increased age of the cohort and corresponding increase of youth endorsing experimentation with alcohol.
- At Wave 1, the mean age of first sip of alcohol was 13 years, with a range of 9-15 years old.
- At Wave 2, the mean age of first sip of alcohol was 14 years, with a range of 10-17 years old.
- At Wave 3, the mean age of first sip of alcohol was 14 years, with a range of 10-18 years old.
Fifty-one percent of youth who consumed alcohol in the past 12 months, across time, said that they did not drink alcohol in the last 30 days.
| Number of days at least one drink of alcohol consumed in the past 30 days among youth who had alcohol in the past 12 months– Child respondent | Wave 1 (n = 182) |
Wave 2 (n = 188) |
Wave 3 (n = 264) |
| 0 days | 45% | 57% | 51% |
| 1 day | 28% | 16% | 20% |
| 2 days | 12% | 12% | 15% |
| 3 days | 6% | 4% | 6% |
| 4-9 days | 7% | 8% | 5% |
| 10-19 days | 1% | 2% | 3% |
| 20-30 days | 1% | <1% | <1% |
Most youth who reported using alcohol did so infrequently. In fact, among youth who consumed alcohol in the past 12 months, the percentage of youth who reported having had one drink of alcohol in the past 30 days decreased from 28% at Wave 1 to 20% at Wave 3. Rates for those who reported drinking on 2 or more days were stable. Interestingly, despite the aging of the cohort, the percentage of youth who drank alcohol in the past 30 days was relatively stable over time.
Furthermore, among youth who consumed alcohol in the past 12 months, binge drinking was rare.
| Number of days 5 or more alcoholic drinks consumed – Child respondent | Wave 1 (n = 182) |
Wave 2 (n = 188) |
Wave 3 (n = 264) |
| 0 days | 81% | 86% | 84% |
| 1 day | 11% | 5% | 9% |
| 2 days | 4% | 4% | 1% |
| 3 days | 2% | 1% | 1% |
| 4-9 days | <1% | 2% | 2% |
| 10-19 days | 2% | <1% | 2% |
| 20-30 days | — | <1% | <1% |
Less than 20% of youth who reported drinking in the past year ever consumed more than five alcoholic drinks consecutively in the past year. Of the youth who reported binge drinking in the past 30 days, most (5%-11%) reported doing so on one day.
Cigarettes:
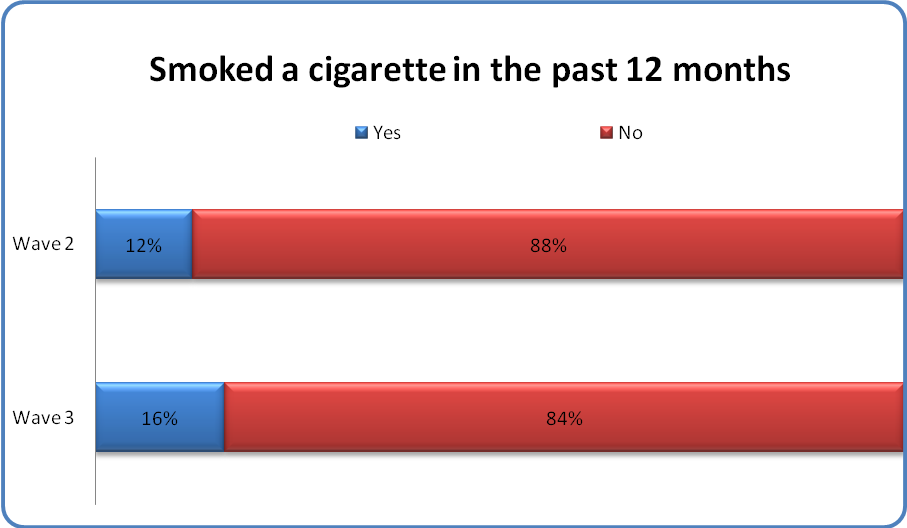
Past year cigarette smoking was the second most commonly used substance reported by the cohort.
One of every 7 youth reported smoking a cigarette in the last year.+
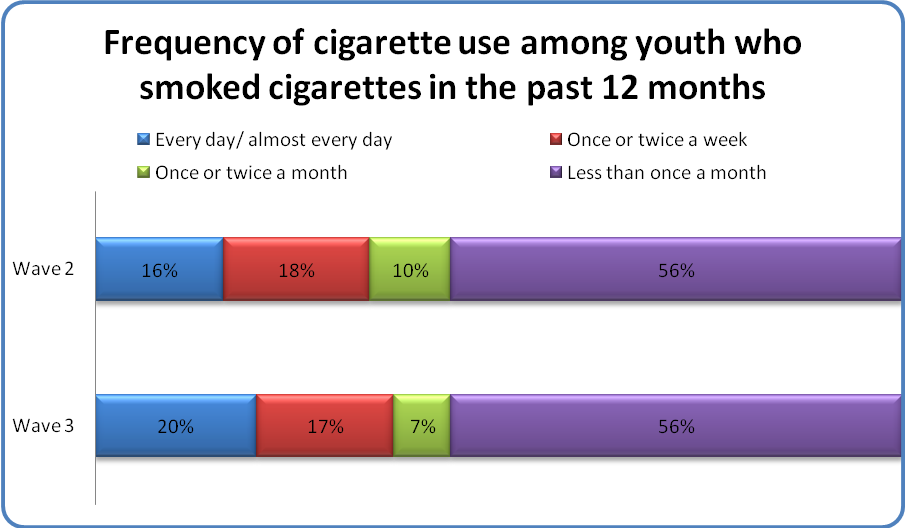
Rates of cigarette use were stable over the 24-month period from Wave 2 to Wave 3 for youth who reported smoking cigarettes in the past 12 months (NWave2 = 132; NWave3 =162).1 Most youth (56%) smoked cigarettes less than once a month. Of concern, about 1 of every 5 youth who smoked cigarettes reported doing so daily.
+This question was asked only at Waves 2 and 3.
Marijuana:
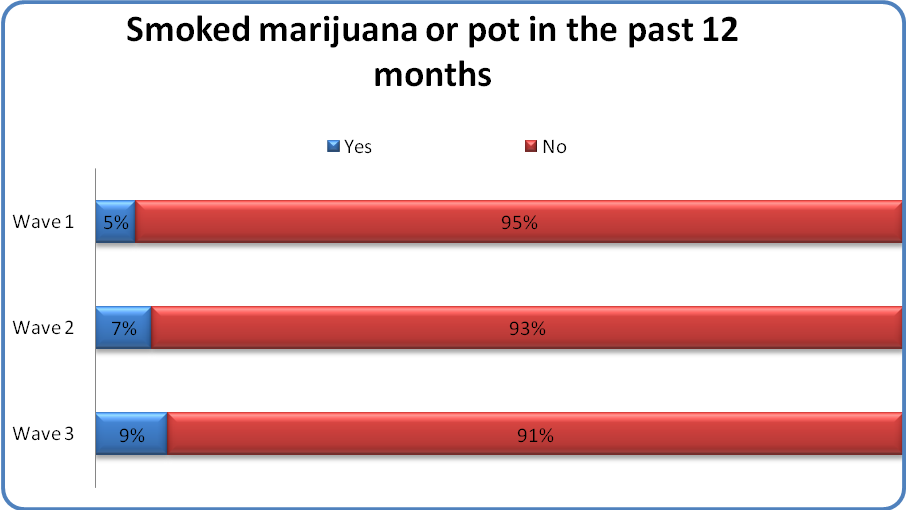
Smoking marijuana or pot in the past 12 months was the third most commonly reported substance used by the cohort.
Less than 1 of every 10 youth reported smoking marijuana or pot in the past 12 months.
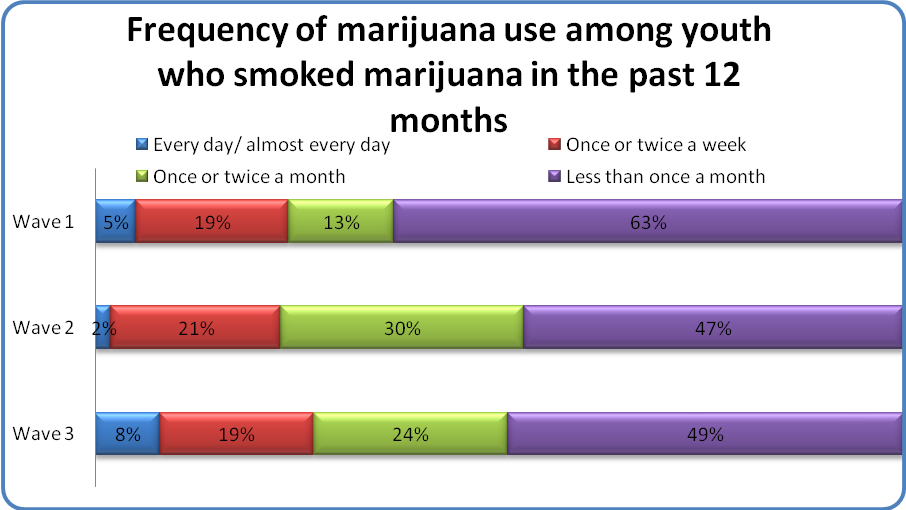
Among youth who reported smoking marijuana in the past 12 months (NWave1 = 68; NWave2 = 68; NWave3 = 91), similar to cigarette use, the majority smoked marijuana less than once a month (49%-63%) (see Figure on page 21).
Over time, the percentage of youth who smoked daily increased slightly (from 5% to 8%) and the percentage of youth who smoked less than once a month decreased (from 63% to 49%). Youth were more likely to be more frequent smoking of marijuana compared to cigarettes, suggesting that this substance may be more acceptable for repetitive use than cigarettes within adolescent culture.
Inhalant Use:
Inhalants were uncommonly reported by the cohort.
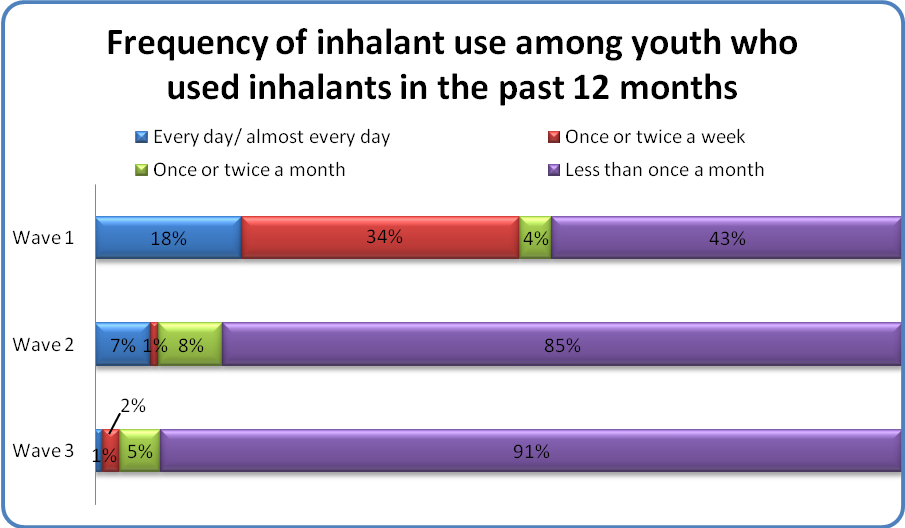
Use of inhalants like whippets, glue, and paints were uncommon in the cohort – especially compared to alcohol, cigarettes, and marijuana. Rates were consistently low over time.
Among youth who reported using inhalants like whippets, glue, and paints in the past 12 month (NWave1 = 29; NWave2 = 33; NWave3 = 35), the vast majority did so less than once a month. There was a notable decline in youth who reported more frequent inhalant use. This shift may be partially explained by the small percentage of youth (1-3% of the entire cohort) who endorsed this behavior, making estimates somewhat unstable.
Use of other drugs:
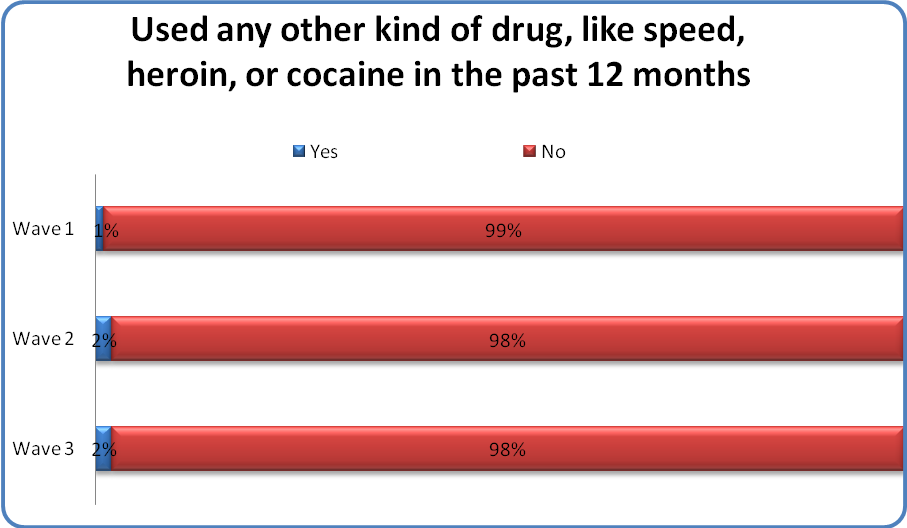
Use of ‘hardcore’ drugs like speed, heroin, or cocaine was the least commonly used by youth.
One to 2% of youth reported using any other kind of drug, like speed, heroin, or cocaine in the past 12 months (see Figure above). Similar to inhalant use, use of ‘any other kind of drug’ were consistently low over time.
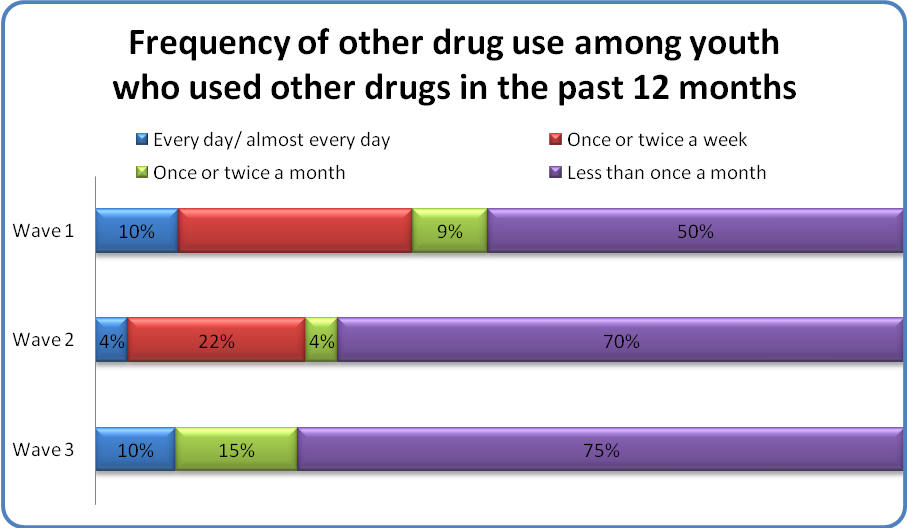
As shown in the Figure above, half of youth at Wave 1 who said they used other drugs like speed, heroin, or cocaine in the past 12 months (NWave1 = 18; NWave2 = 20; NWave3 = 25) used those drugs less than once a month, this increased to 3 of every 4 youth by Wave 3. A mirrored decrease was observed in the percentage of youth these types of drugs once or twice a week from 28% at Wave 1 to 0% at Wave 3.